 Virtualization is a technique for wireless operators seeking to reduce capital costs and increase flexibility in their networks. To date, virtualization has focused on hardware-based functions like routing, firewalls and content caching. Cloud Radio Access Network (Cloud-RAN, or C-RAN) provides a way to extend this concept to mobile base station hardware because it centralized the base station function for a large number of radios into a single location.
Virtualization is a technique for wireless operators seeking to reduce capital costs and increase flexibility in their networks. To date, virtualization has focused on hardware-based functions like routing, firewalls and content caching. Cloud Radio Access Network (Cloud-RAN, or C-RAN) provides a way to extend this concept to mobile base station hardware because it centralized the base station function for a large number of radios into a single location.
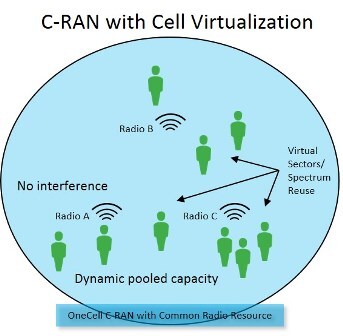
Cell virtualization – an emerging capability enabled by C-RAN architectures – extends the concept and benefits of virtualization beyond hardware and into the airwaves. It provides a way for wireless operators to deliver substantially more capacity on a given amount of spectrum. This in turn relieves them of, or delays, the need to acquire costly additional spectrum. Like network functions virtualization (NFV), cell virtualization also delivers capacity more dynamically and efficiently, where and when it is needed.
C-RAN-enabled cell virtualization gives operators the ability to re-use spectrum many times over within the footprint of a single cell. Because the C-RAN baseband unit “knows” the location of each user, it can determine when two users are sufficiently isolated from one another to serve them at the same time reusing the same LTE resources. The result is multi-cell capacity without border interference.
Cell virtualization achieves the multi-sector capacity of many standalone small cells, with up to a 1,000 percent increase in user data rates at the cell edge – an order of magnitude improvement – through the elimination of border interference. It also enables more dynamic and efficient use of a scarce and costly resource: spectrum. Considering operators have spent $107 billion on spectrum purchases in the last three years, cell virtualization can help operators leverage their investments by dramatically improving spectral efficiency. And device battery life improves because the user device need only track a single cell and because they transmit at a lower power level.
The Smart Reuse feature of CommScope’s OneCell Cloud-RAN Small Cell Solution is the embodiment of the cell virtualization concept. The Small Cell Forum has named CommScope as a finalist in its Small Cell Forum Industry Awards in the category of “Small cell technology or business case innovation” for the cell virtualization concept. Light Reading also recently announced that CommScope is a finalist for its Leading Lights Awards 2016 in the category of Most Innovative NFV Product Strategy (Vendor) for cell virtualization.
You can learn more about cell virtualization at the upcoming Small Cells World Summit in London, May 10-12. I will be speaking about it in the Wednesday morning “Toward 5G” track, and we will be demonstrating cell virtualization on our OneCell C-RAN small cells in stand 43. Cell virtualization is a solution to capacity needs inside of buildings today as well as one of the innovations that will lay the foundation for 5G.