Aurora Networks® (ANS) and RUCKUS® Networks are now Vistance Networks
What is Fiber to the Premises?
Fiber to the Premises (FTTP) is a broadband network architecture that delivers fiber-optic connectivity directly to homes and businesses. Unlike traditional copper-based networks, FTTP provides high-speed internet access with enhanced bandwidth and reliability.
Key Takeaways
-
Direct fiber connectivity: FTTP delivers fiber-optic internet directly to homes and businesses, offering faster and more reliable service than traditional copper-based networks.
-
Includes FTTH and FTTB: FTTP is a broad term that covers both Fiber to the Home (FTTH) for individual residences and Fiber to the Building (FTTB) for multi-dwelling units or commercial properties.
-
Superior performance and durability: FTTP provides high-speed data transmission, low latency, and greater network capacity, while fiber cables are more resistant to environmental wear than copper.
-
Supports modern digital demands: The architecture is ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications like streaming, cloud computing, and smart home technologies.
-
Future-ready infrastructure: FTTP is a key component in expanding broadband access and building next-generation communication networks, widely adopted by service providers for long-term scalability.

Types of FTTP Deployments
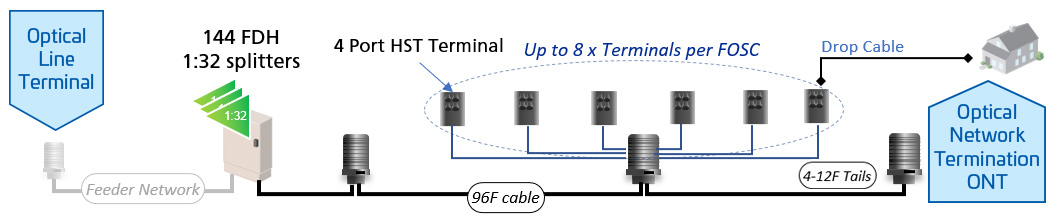
FTTP is often used as a general term encompassing both Fiber to the Home (FTTH) and Fiber to the Building (FTTB). FTTH refers to fiber connections that reach individual residences, while FTTB serves multi-dwelling units or commercial buildings.
Advantages of FTTP
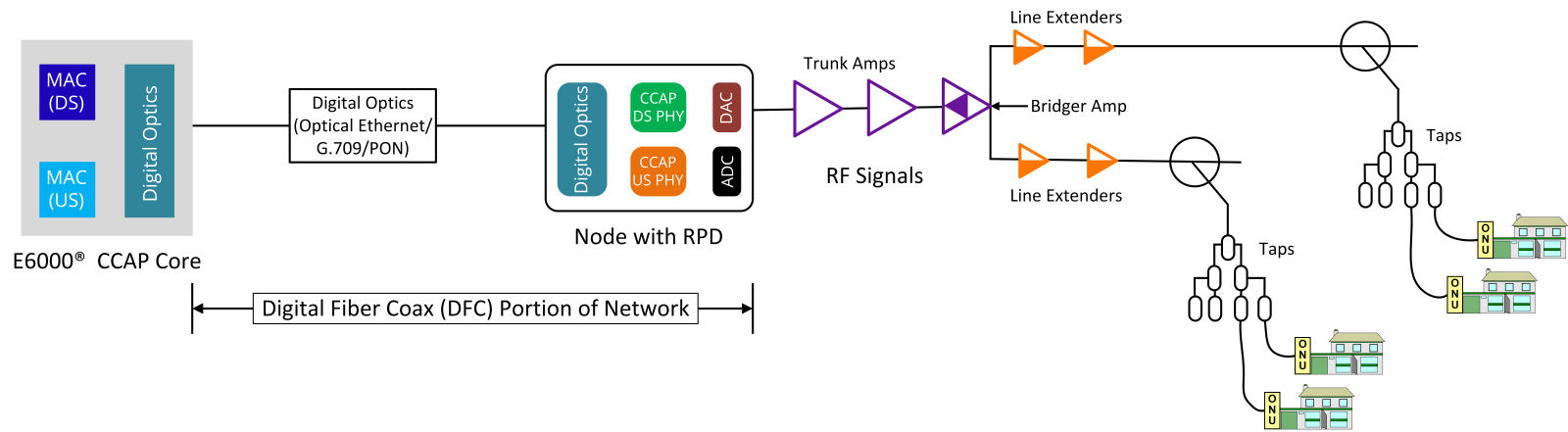
One of the key advantages of FTTP is its ability to deliver higher data transmission speeds, lower latency, and increased network capacity all whilst reducing operational costs and power consumption. This makes it ideal for supporting modern applications such as streaming, cloud computing, and smart home technologies. Additionally, fiber-optic cables offer greater durability and resistance to environmental factors compared to copper-based alternatives.
FTTP in Network Infrastructure
As demand for high-speed internet and digital services continues to grow, FTTP plays a vital role in expanding broadband access and enabling next-generation communication networks. It is widely adopted by service providers seeking to deliver reliable, future-ready connectivity.