Aurora Networks® (ANS) and RUCKUS® Networks are now Vistance Networks
What Are the Benefits of 10G?
Introduction to 10G Broadband
10G broadband is a next-generation network technology designed to provide internet speeds of 10 gigabits per second (Gbps)—ten times faster than current broadband speeds. Unlike 5G, which refers to the fifth generation of mobile broadband, 10G focuses on enhancing fixed broadband networks to support increasing demands for high-speed, low-latency connectivity.
Key Takeaways
-
Significantly faster internet speeds: 10G broadband offers symmetrical 10 Gbps speeds, enhancing both uploads and downloads—ideal for data-heavy activities like cloud computing, VR, and HD streaming.
-
Lower latency for real-time experiences: The technology supports ultra-low latency, which can improve responsiveness in applications such as online gaming, telemedicine, and autonomous systems.
-
Greater network reliability and security: Advanced encryption and resilient infrastructure contribute to more stable connections and stronger protection against cyber threats.
-
Scalable infrastructure evolution: 10G enables a gradual upgrade path using existing Hybrid Fiber Coax networks, supported by technologies like Full Duplex DOCSIS and Extended Spectrum DOCSIS.
-
Support for future digital demands: As digital applications grow more complex, 10G broadband helps networks adapt to evolving needs across industries without requiring complete overhauls.
Enhanced Speed and Capacity
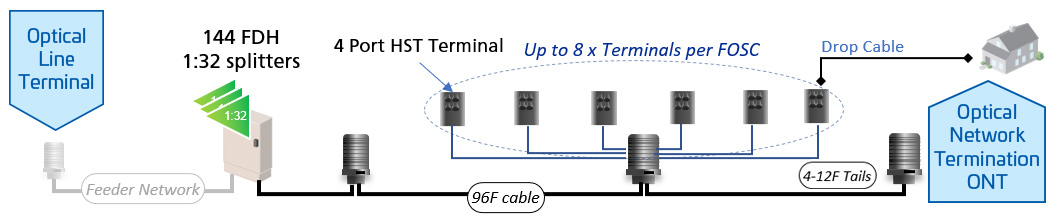
One of the primary benefits of 10G broadband is its ability to deliver symmetrical speeds, meaning both upload and download speeds are significantly improved. This is crucial for applications such as cloud computing, virtual reality, and high-definition video streaming, which require seamless data transmission. Additionally, fiber densification plays a key role in expanding network capacity, helping operators meet growing bandwidth demands.
Ultra-Low Latency for Real-Time Applications
Latency—the delay in data transmission—is a critical factor for applications such as online gaming, telemedicine, and autonomous vehicles. 10G broadband significantly reduces latency, enabling real-time interactions and improving overall user experience. This is also particularly beneficial for industries that rely on instantaneous data processing, such as financial services and remote collaboration.
Improved Network Reliability and Security
With 10G broadband, networks are designed to be more resilient and secure, reducing the risk of service disruptions and cyber threats. The technology incorporates advanced encryption and security protocols, helping to keep that data remains protected while being transmitted across the network. This is essential for businesses and individuals who rely on secure connections for sensitive transactions and communications.
Future-Proofing Infrastructure
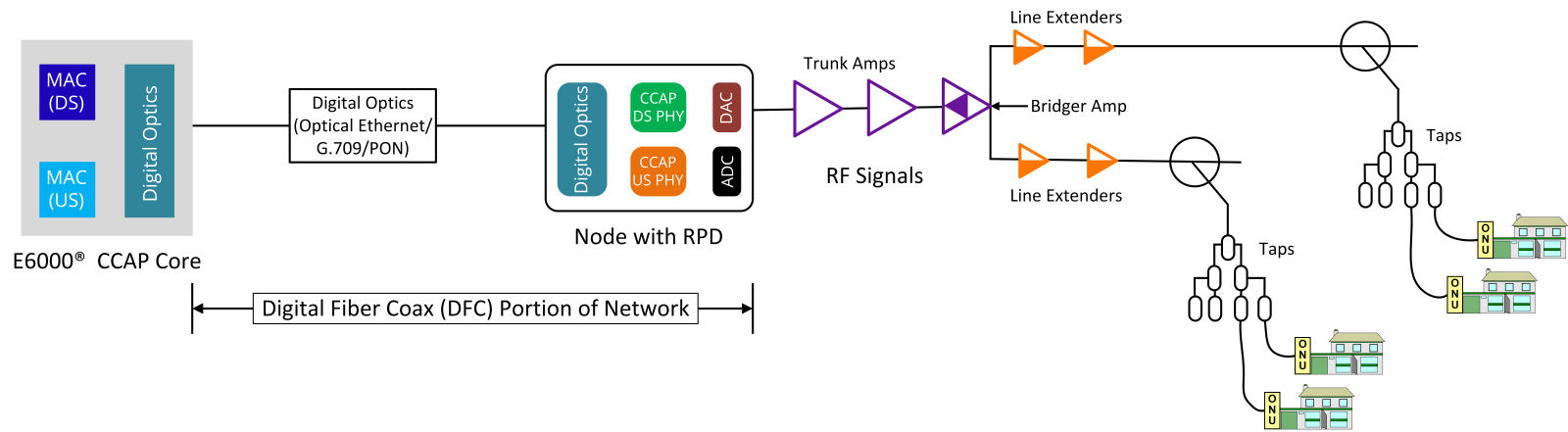
10G broadband is not a single upgrade but rather a gradual transformation of existing network infrastructure. By leveraging Hybrid Fiber Coax (HFC) networks, operators can transition to 10G without completely overhauling their systems. Technologies such as Full Duplex DOCSIS1 (FDX) and Extended Spectrum DOCSIS (ESD) enable essentially seamless integration, allowing networks to evolve while maintaining cost efficiency.
Conclusion
The shift to 10G broadband represents a significant leap forward in internet connectivity, offering higher speeds, lower latency, enhanced security, and improved reliability. As demand for data-intensive applications continues to grow, 10G broadband helps networks remain future-ready, supporting innovation and digital transformation across various industries.
Related Links
1 DOCSIS is a trademark of Cable Television Laboratories, Inc.
© 2025 CommScope, LLC. All rights reserved. CommScope and the CommScope logo are trademarks of CommScope and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. For additional trademark information see https://www.commscope.com/trademarks. Wi-Fi, Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7 are trademarks of the Wi-Fi Alliance. All product names, trademarks and registered trademarks are property of their respective owners.