Aurora Networks® (ANS) and RUCKUS® Networks are now Vistance Networks
What is EPON?
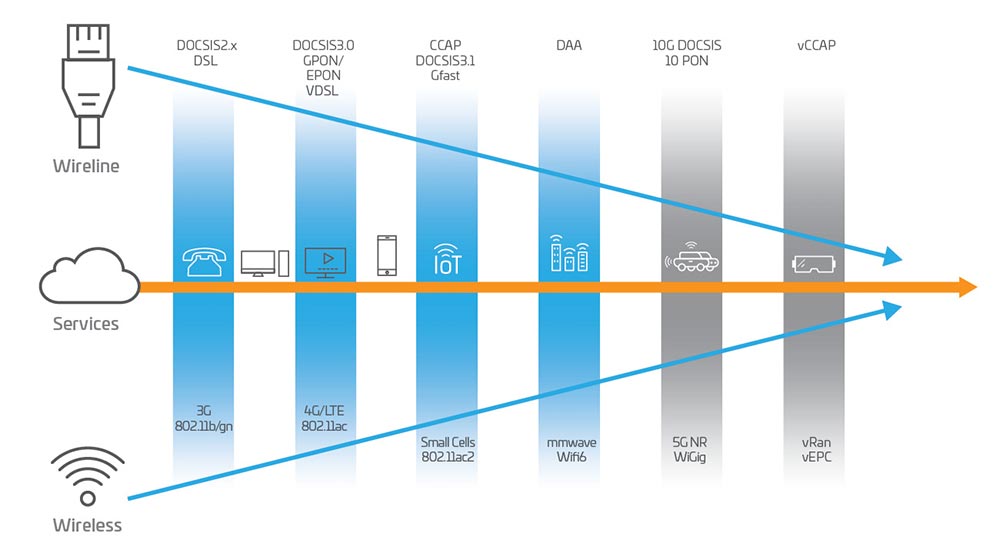
Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON) is a fiber-optic broadband technology that utilizes Ethernet protocols to deliver high-speed internet access. EPON is a type of Passive Optical Network (PON) enabling symmetrical data transmission, making it ideal for both residential and commercial applications.
Key Takeaways
-
Fiber-based broadband using Ethernet protocols: EPON delivers high-speed internet over fiber-optic networks using standard Ethernet, making it suitable for both residential and commercial use.
-
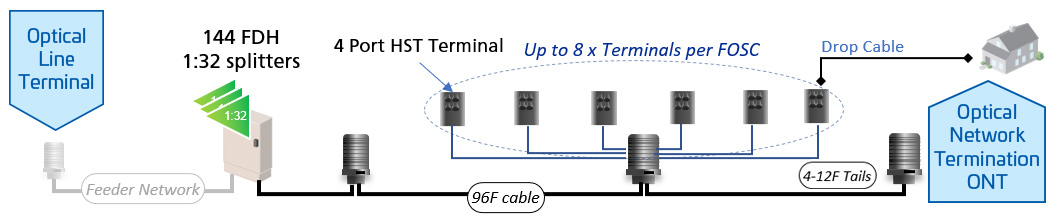
Efficient point-to-multipoint architecture: An Optical Line Terminal (OLT) connects to multiple Optical Network Units (ONUs) via passive splitters, enabling cost-effective and scalable data distribution without active components.
-
Symmetrical high-speed connectivity: EPON supports both 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps speeds, offering reliable and consistent performance for upstream and downstream traffic.
-
Simplified integration and management: Leveraging Ethernet standards allows for easier network deployment and maintenance compared to other PON technologies like GPON.
-
Flexible deployment options: EPON can be implemented in centralized or distributed architectures, giving service providers the ability to tailor networks to specific service demands and infrastructure conditions.
Key Features of EPON
EPON operates using a point-to-multipoint architecture, where an Optical Line Terminal (OLT) connects to multiple Optical Network Units (ONUs) through passive optical splitters. This setup allows efficient data distribution without requiring active electronic components in the transmission path. EPON supports 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps speeds, helping to provide enhanced, reliable and scalable connectivity.
Advantages of EPON
EPON offers several benefits, including high bandwidth capacity, low latency, and cost-effective deployment. By leveraging Ethernet-based protocols, EPON helps simplify network integration and management, making it a preferred choice for service providers looking to expand fiber-optic infrastructure.
EPON vs. Other PON Technologies
Compared to GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network), EPON provides a more straightforward implementation due to its reliance on Ethernet standards. While GPON uses Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), EPON employs packet-based transmission, enhancing flexibility and efficiency in data handling.
Deployment Considerations
Service providers adopting EPON must assess network compatibility, including OLT and ONU configurations. EPON can be deployed in centralized or distributed architectures, allowing operators to optimize network performance based on service demands.
Related Links