Aurora Networks® (ANS) and RUCKUS® Networks are now Vistance Networks
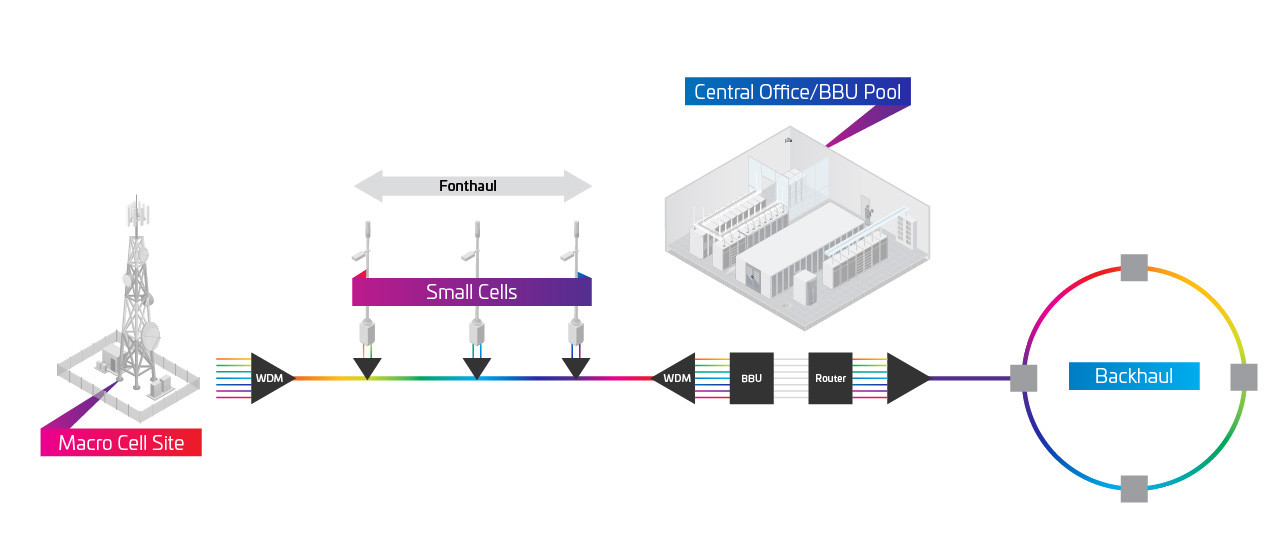
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDMs) and de-multiplexers combine multiple signals for transport on a single fiber, and separate combined signals for distribution to multiple destinations—increasing the bandwidth available on your existing fiber. They can be applied in core and metro networks, transport networks, hybrid fiber cable (HFC) distributed access architectures and wireless transport, enabling true converged all optical IP communication.
WDM solutions require no power or additional fiber installation, making them quick and easy to install and maintain. The ITU.T has standardized wavelength channels in a Course and Dense WDM grid, offering a path to exploit the full optical spectrum in a single fiber, with the possibility to overlay signals, including coexistence of ethernet communications with PON technology.
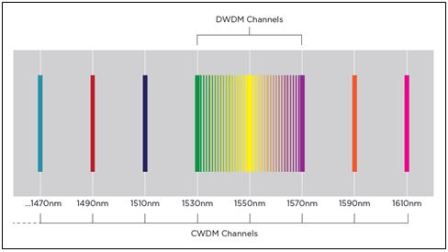
Coarse Wave Division Multiplexing (CWDM) is standardized to have 18 different wavelength channels with a spacing of 20 nanometers (nm) starting at 1270 nm and ending at 1610 nm. Most systems use the eight channels in the upper band (eight channels from 1470 nm to 1610 nm). The advantage of CWDM systems is that it is always possible to upgrade at a later point in time to limit the installation cost on day one. The wider channel spacing places less stringent requirements on the lasers, which allows use of less expensive lasers without temperature controllers.
Dense Wave Division Multiplexing (DWDM) devices are mostly used in the core networks to extend over very long distances and where more wavelengths are required between sites. The 40 wavelength channels are distributed in the C-band from 1530 nm to 1570 nm. If required, DWDM can be “over-layed” on a CWDM infrastructure to increase capacity.
CommScope’s WDM portfolio includes a variety of form factors, optimal for a wide range of inside plant (ISP) and outside plant (OSP) applications. For example, CommScope’s LGX or NG4 ISP Multiplexing Modules can be used in the headend or central office facility to multiplex signals. They can be paired with FOSC or FIST fiber optic closures containing the matching De-mux modules, or use add-drop solutions optimal for daisy chaining.
With CommScope’s WDM, operators can:
- Support high-speed, high-capacity throughput with low latency
- Improve quality of service
- Make the most out of their fiber investments, for fixed and mobile access, optical transport
- Deploy GPON, CPRI and Ethernet traffic on the same network or fiber strand
- Migrate easily from 1G to 100G, 400G and higher – using latest technologies such as coherent optic transceiver technology
Products
-
Download
Specification Guide: DWDM
CommScope’s DWDM devices support network performance upgrades and increases the bandwidth available on your existing fiber network infrastructure.
-
Download
Brochure: OCC1D - Add/Drop Single Channels
Field-installable Dense wavelength division multiplexing devices
-
Download
White Paper: Next-generation WDM technologies
Next-generation WDM technologies offer choices to meet rising bandwidth demands.