Cost is one of the most important factors influencing an end user’s adoption of any emerging technology.
Recently, I conducted some research on the cost of 10, 40 and 100 Gigabit Ethernet (GbE). To have the same level of comparison, my research was focused on the cost of optical transceivers for end users. I gathered all the cost information on August 31, 2011 from the website www.sanspot.com. If you did not know, an optical transceiver is a pluggable electronic module that transmits and receives signals over optical fiber media.
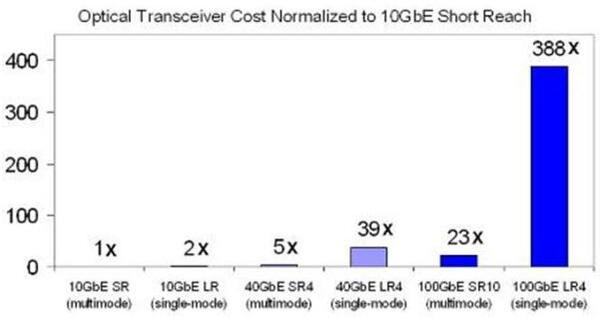
The horizontal axis of the Chart 1 shows the IEEE standard 10, 40 and 100GbE technologies across multimode and single-mode fiber. The vertical axis is the cost of the corresponding optical transceivers normalized to the one of 10GbE short reach. The 10GbE SR (short reach) is the IEEE standard that specifies 10GbE operations over multimode fiber while LR stands for long reach.
As Chart 1 illustrates, 40 and 100GbE optical transceivers over multimode fiber currently are five and 23 times the cost of 10GbE short reach, respectively. Also, 40 and 100GbE transceivers over single-mode fiber currently are 39 and 388 times the cost of 10GbE SRs. Chart 1 clearly illustrates that 40/100GbE is more cost-effectiveover multimode fiber than over single-mode fiber.
So, what does this all prove? Well, it proves that OM3/OM4 multimode fiber is optimal for 40/100GbE application in data center environment because the support distance of OM3/OM4 fiber cabling can cover most of the cable reach needs in data centers.
Chart 2 illustrates that SYSTIMAX LazrSPEED exceeds the standards and provides end users extra flexibility covering most of the cable needs data centers require and demand.
How has LazrSPEED added benefits to your data centers?