Aurora Networks® (ANS) and RUCKUS® Networks are now Vistance Networks
How Do You Bridge the Digital Divide?
The “digital divide” refers to the gap between individuals and communities that have access to modern information and communication technology and those that do not. This disparity affects education, economic opportunities, and social inclusion, making it a critical issue to address.
Key Takeaways
-
Broadband expansion is foundational: Extending internet infrastructure to underserved rural and low-income areas is essential for ensuring equitable access to digital services.
-
Education-focused initiatives are critical: Programs that provide students with internet-enabled devices, digital literacy training, and access points like Drive-Fi help bridge learning gaps caused by lack of connectivity.
-
Collaboration drives progress: Public-private partnerships involving governments, tech companies, and community organizations are vital for funding and implementing sustainable digital inclusion strategies.
-
Future technologies offer new solutions: Innovations such as private LTE networks and enhanced cellular coverage can further improve connectivity in hard-to-reach areas.
-
Digital inclusion is an ongoing priority: Bridging the digital divide requires continuous effort to adapt to evolving technologies and ensure all communities benefit from digital opportunities.

Expanding Broadband Access
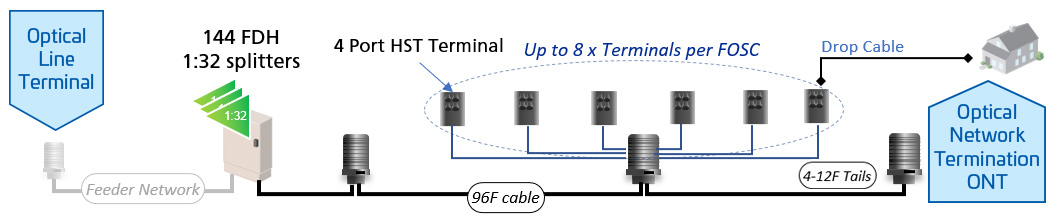
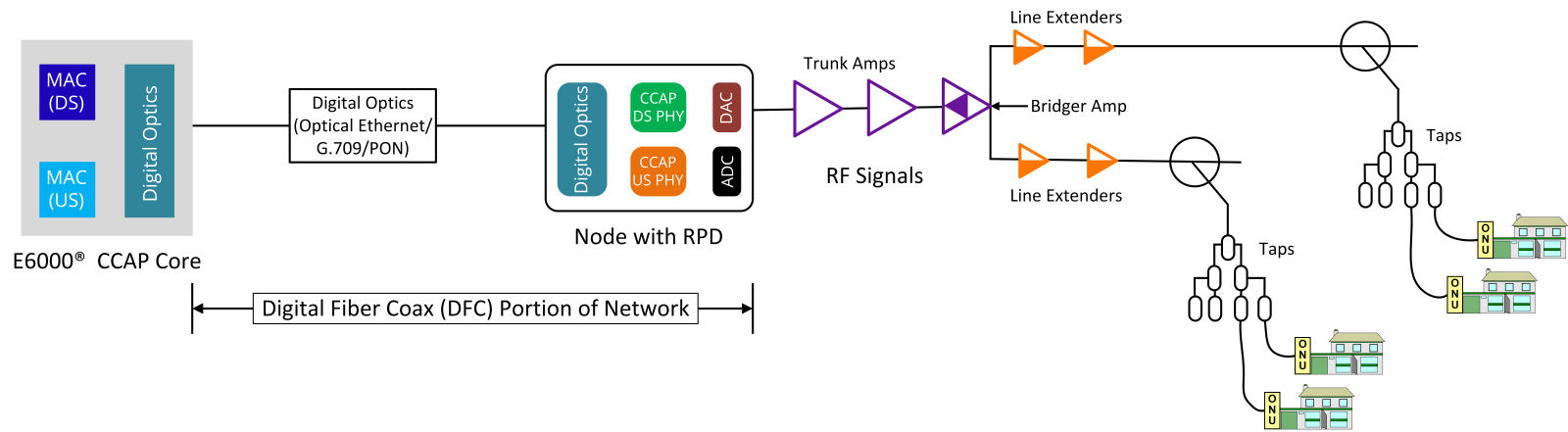
One of the largest challenges to bridging the digital divide is expanding and deploying infrastructure to underserved areas. Many underserved areas, particularly rural and low-income communities, lack reliable internet access. Network providers and government agencies collaborate to deploy broadband networks, working to enhance connectivity for all.
Enhancing Digital Equity in Education
Schools play a crucial role in addressing digital inequities. Many students lack home internet access, making it difficult to complete assignments or engage in online learning. Initiatives such as Drive-Fi, where Wi-Fi® is deployed in parking lots and public spaces, help students access educational resources. Additionally, providing internet-enabled devices and digital literacy training enables students to fully participate in digital learning.

Public and Private Sector Collaboration
Closing the digital divide requires cooperation between governments, private enterprises, and community organizations. Investments in digital infrastructure, policy initiatives, and funding programs help create sustainable solutions for long-term connectivity.
Future Considerations
As technology continues to evolve, addressing the digital divide remains an ongoing effort. Emerging solutions such as private LTE networks and improved cellular coverage can further enhance connectivity in underserved areas. By prioritizing digital inclusion, communities can ensure equitable access to technology and the opportunities it provides.
Addressing the digital divide is an ongoing effort that requires prioritizing digital inclusion to create more equitable access to technology and the opportunities it provides. By expanding broadband access, enhancing digital equity in education, fostering public and private sector collaboration, and considering future technological advancements, communities can work towards closing the digital gap and promoting social inclusion.