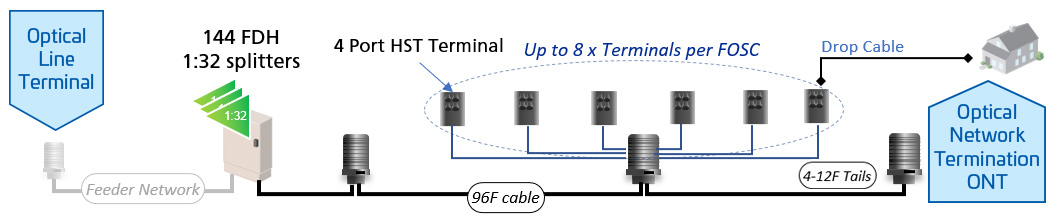
Aurora Networks® (ANS) and RUCKUS® Networks are now Vistance Networks
What are the Benefits of Distributed Access Architecture?
Decentralized Network Processing
Distributed Access Architecture (DAA) decentralizes key network functions by moving processing capabilities from a centralized headend to the edge of the network. This shift allows for more responsive and efficient broadband service delivery.
Key Takeaways
- Digital Ethernet-based connections replace analog links, increasing bandwidth capacity and making more efficient use of the available spectrum.
- Network designs become more flexible and scalable, allowing better use of existing fiber infrastructure.
- Operational complexity and maintenance costs are reduced, thanks to the modular and virtualized nature of DAA systems.
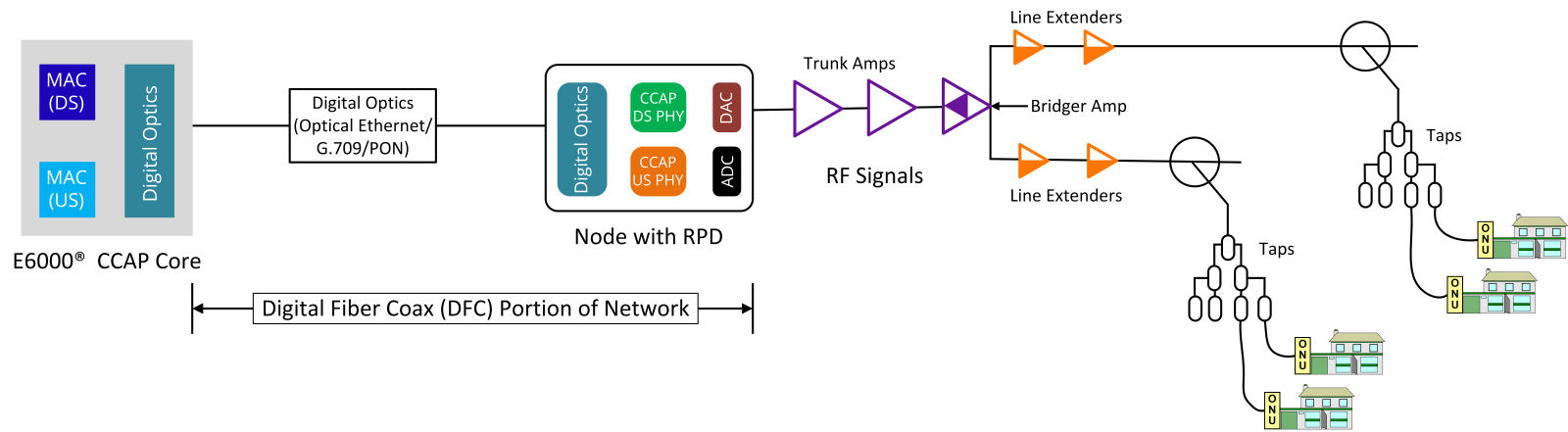
Improved Bandwidth and Spectral Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of DAA is its ability to improve spectral efficiency. By replacing analog fiber links with digital Ethernet-based connections, DAA supports higher data throughput and more efficient use of available spectrum.
Operational and Maintenance Advantages
By virtualizing and decentralizing network functions, DAA simplifies network operations and reduces maintenance complexity. Additionally, the modular nature of DAA allows for easier upgrades and faster deployment of new services, contributing to lower operational costs over time.