Aurora Networks® (ANS) and RUCKUS® Networks are now Vistance Networks
What Is a Virtual Network Manager?
A virtual network manager is a software-based system designed to oversee and control virtualized network functions and infrastructure. It plays a central role in managing the lifecycle of virtual network elements, including provisioning, monitoring, scaling, and troubleshooting. In broadband environments, a virtual network manager helps operators coordinate complex, distributed systems by providing centralized visibility and control over virtualized components.
Key Takeaways
- A virtual network manager oversees virtualized network functions, providing centralized control over distributed, software-based infrastructure.
- It enables dynamic service deployment and scaling, allowing operators to manage network resources more flexibly without relying on dedicated hardware.
- Integration with SDN and telemetry systems allows for real-time performance monitoring and policy-based automation across the network.
- It simplifies operations and reduces complexity, especially in environments transitioning to cloud-native or distributed access architectures.
- Virtual network managers support both fiber and HFC networks, helping coordinate virtualized headend, Remote PHY devices, and other disaggregated components.

Integration with Virtualized Platforms
In the context of CommScope’s broadband solutions, the virtual network manager works alongside platforms like the vBNG Evo (virtual Broadband Network Gateway). It supports the orchestration of user and control planes across distributed locations, enabling operators to scale services dynamically. The virtual network manager also facilitates the deployment of new services by managing software-based network functions without the need for dedicated hardware.
Support for SDN and Telemetry
A virtual network manager often integrates with Software-Defined Networking (SDN) frameworks to provide northbound orchestration and policy control. It also gathers telemetry data from across the network, offering insights into performance, usage patterns, and potential issues. This data-driven approach allows operators to make informed decisions and optimize network behavior in real time.
Operational Efficiency and Scalability
By abstracting and automating network management tasks, a virtual network manager reduces operational complexity and supports more agile service delivery. It allows operators to start with small-scale deployments and expand to large, cloud-based environments as needed. This flexibility is particularly valuable in modern broadband networks that must adapt quickly to changing user demands and technology standards.
Applications in Fiber and HFC Networks
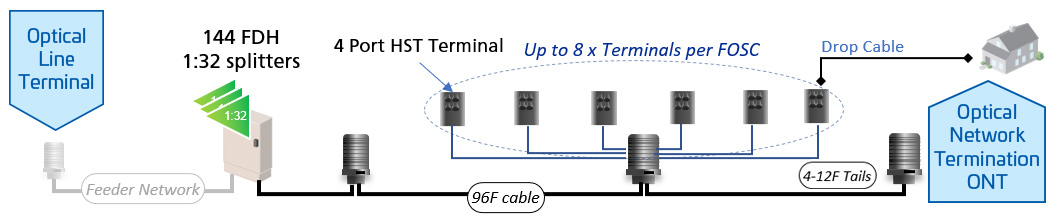
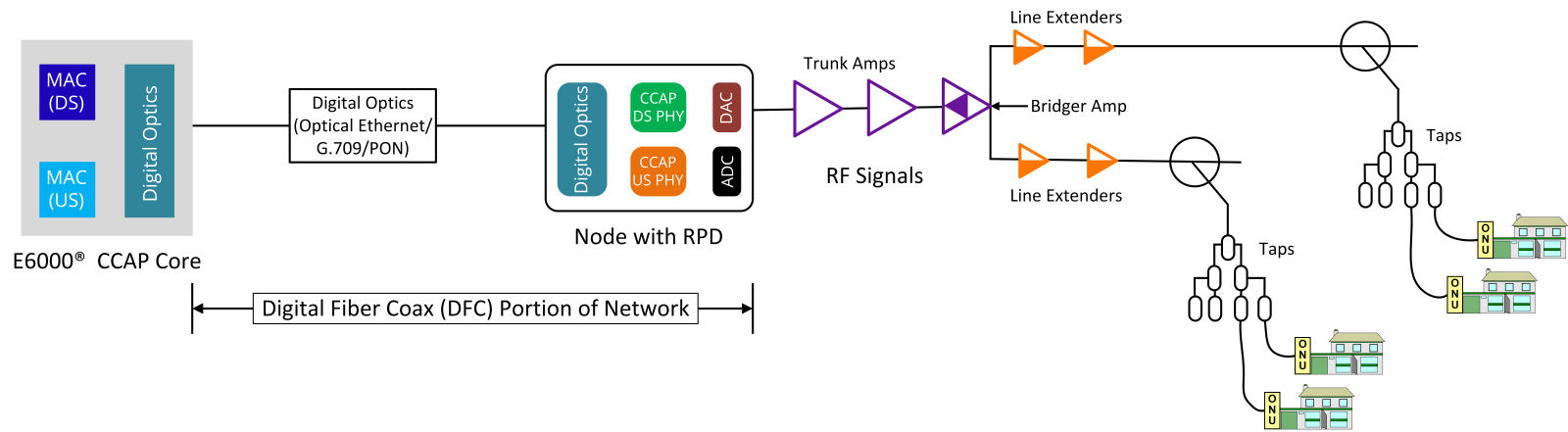
Virtual network managers are used in both fiber and Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial (HFC) networks to streamline operations and support distributed access architectures. They help manage virtualized headend, remote PHY devices, and other disaggregated components, making it easier to deploy and maintain next-generation broadband services across diverse network environments.
CommScope Related Links
Virtualization – The Virtual Headend