Aurora Networks® (ANS) and RUCKUS® Networks are now Vistance Networks
What is Broadband Connectivity?
Broadband connectivity refers to the infrastructure required to provide access to high speed, low latency internet that enables the transmission of large amounts of data efficiently. Unlike traditional dial-up connections, broadband provides continuous access to the internet, supporting various applications such as streaming, online gaming, and cloud computing.
Key Takeaways
-
Broadband enables high-speed, always-on internet: Unlike dial-up, broadband supports continuous access and handles large data volumes efficiently, powering activities like streaming, gaming, and cloud computing.
-
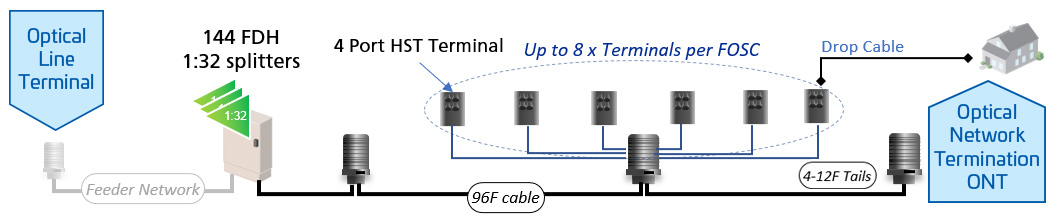
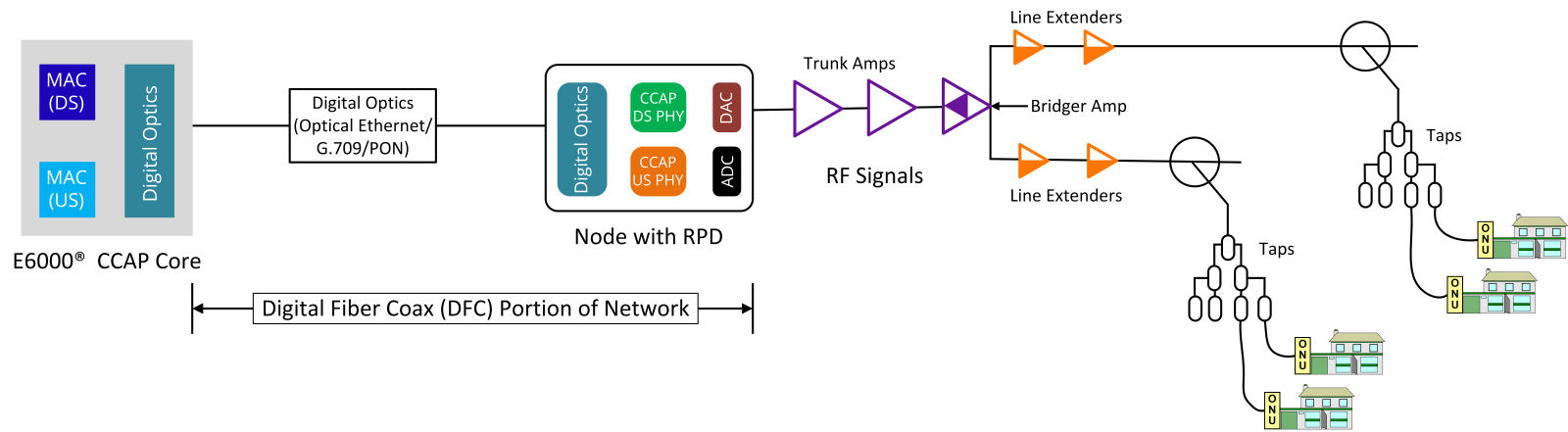
Multiple technologies deliver broadband: Options include fiber optics (fastest and most reliable), cable, DSL, and wireless solutions like satellite and mobile networks, each suited to different environments and needs.
-
Essential for modern life: Broadband supports economic development, education, healthcare (e.g., telemedicine), and communication, making it a foundational utility in today’s digital society.
-
Deployment faces real-world challenges: Infrastructure costs, geographic barriers, and regulatory issues can limit broadband expansion, especially in rural and underserved areas.
-
Innovation is shaping the future: Emerging technologies like 5G, advanced fiber optics, and next-gen satellite internet aim to make broadband faster, more reliable, and accessible to all.
Types of Broadband Technologies
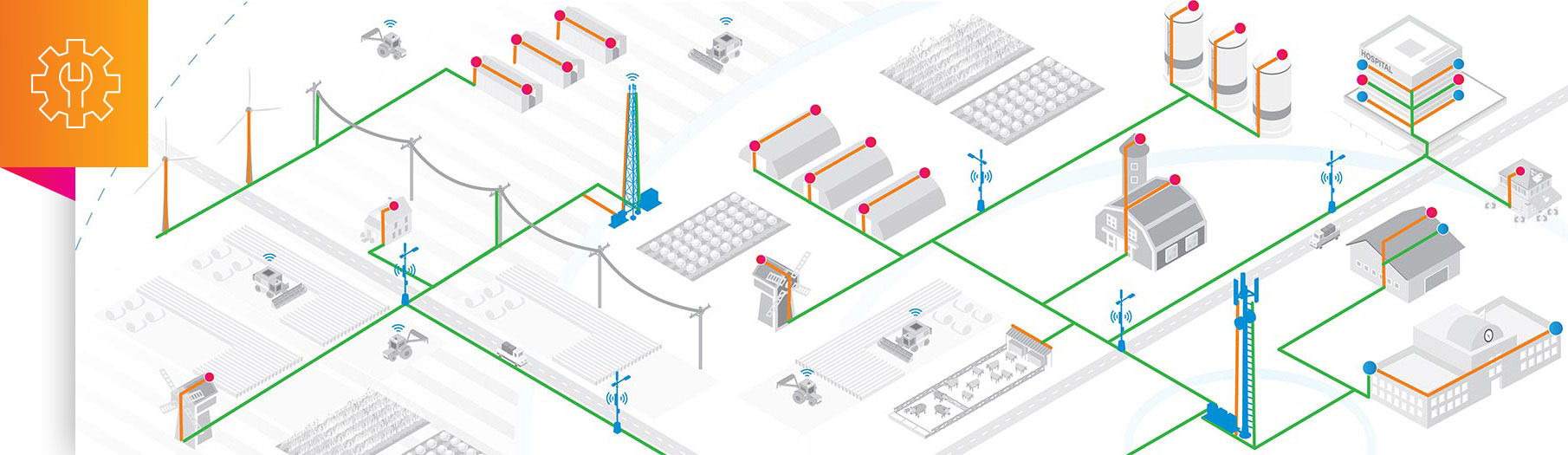
Broadband connectivity can be delivered through multiple technologies, including fiber optics, cable, DSL, wireless, and Satellite networks. Fiber optic broadband offers the highest speeds and reliability, while cable and DSL provide widespread access. Wireless broadband, including satellite and mobile networks, extends connectivity to remote and underserved areas.
Importance of Broadband Connectivity
Broadband connectivity plays a crucial role in modern society, supporting economic growth, education, healthcare, and communication. It enables businesses to operate efficiently, helps students access online learning resources, and allows healthcare providers to offer telemedicine services.
Challenges in Broadband Deployment
Expanding broadband access presents challenges such as infrastructure costs, geographic limitations, and regulatory considerations. Rural and underserved communities often face difficulties in obtaining reliable broadband, requiring targeted initiatives to bridge the digital divide.
Future of Broadband Connectivity
Advancements in broadband technology continue to enhance connectivity, with developments such as 5G networks, next-generation fiber optics, and improved satellite internet solutions. These innovations aim to provide faster, more reliable, and universally accessible broadband services.
Related CommScope Links:
© 2025 CommScope, LLC. All rights reserved. CommScope and the CommScope logo are trademarks of CommScope and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. For additional trademark information see https://www.commscope.com/trademarks. All product names, trademarks and registered trademarks are property of their respective owners.