Aurora Networks® (ANS) and RUCKUS® Networks are now Vistance Networks
What is Cascaded Daisy Chain Architecture?
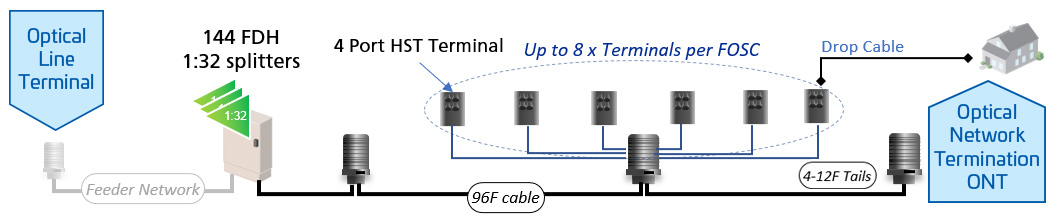
Cascaded Daisy Chain architecture is a ‘lean’ fiber network design that combines elements of cascaded and Distributed topologies to optimize fiber distribution. This approach is used in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) deployments to efficiently connect multiple subscribers while minimizing infrastructure complexity.
Key Takeaways
-
Hybrid Network Design: Cascaded Daisy Chain architecture blends features of cascaded and daisy chain topologies to streamline fiber distribution in FTTH networks.
-
Sequential Splitter Configuration: Optical splitters are arranged in a daisy-chain sequence, where a primary splitter feeds secondary splitters that then connect to individual homes, helping reduce fiber usage.
-
Comparison to Other Architectures: Unlike centralized split models that rely on a single splitter hub, or traditional daisy chains with direct node-to-node links, this approach introduces intermediate splitters for better balance between efficiency and scalability.
-
Infrastructure Efficiency: The design can help lower deployment costs and simplify network layouts by minimizing the amount of fiber and hardware needed across the network.
-
Scalable and Flexible Deployment: Its modular nature supports gradual network expansion, making it suitable for areas where cost-effective growth and adaptable infrastructure are important.
How Cascaded Daisy Chain Architecture Works
In this architecture, fiber splitters are arranged in a sequential, daisy-chain configuration, allowing optical signals to be distributed across multiple locations. A primary splitter connects to secondary splitters, which then route fiber to individual customer premises. This method reduces the amount of fiber required while maintaining network flexibility.
Comparison to Other FTTH Architectures
Cascaded Daisy Chain architecture differs from centralized split architecture, which uses a single-stage splitter in a fiber distribution hub (FDH). It also contrasts with traditional distributed networks, which rely on direct connections between the splitter and the customer premises without intermediate splitters. The cascaded approach balances fiber efficiency with scalability.
Advantages of Cascaded Daisy Chain Architecture
This design offers benefits such as optimized fiber utilization, reduced deployment costs, and greater adaptability for network expansion. It is particularly useful in areas where fiber density needs to be balanced with cost-effective infrastructure planning.
Related CommScope Links: