Aurora Networks® (ANS) and RUCKUS® Networks are now Vistance Networks
What is TAP Architecture?
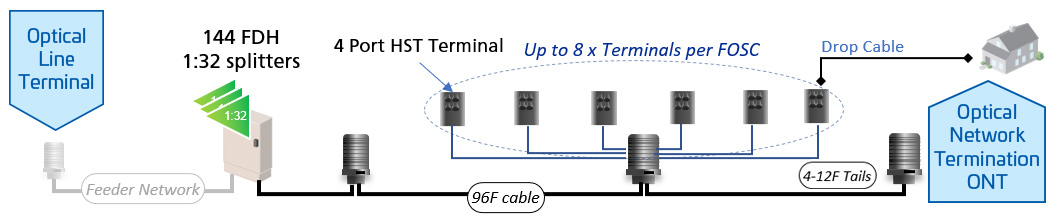
TAP architecture is a “lean” network design approach used in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) deployments, particularly in rural and Low-density areas. It utilizes asymmetrical fiber-optic taps to distribute part of the optical signals to subscribers, reducing the need for traditional splitter cabinets and complex infrastructure.
Key Takeaways
-
Simplified signal distribution: TAP architecture uses fiber-optic taps spliced along a main fiber line to divert portions of the signal to individual subscribers, eliminating the need for centralized splitter cabinets.
-
Efficient for rural and low-density areas: This design is especially effective in regions with challenging terrain or sparse populations, where traditional FTTH infrastructure may be impractical or costly.
-
Reduces infrastructure complexity: By avoiding large distribution cabinets and minimizing splicing, TAP architecture lowers deployment complexity and speeds up installation.
-
Cost-effective and scalable: TAP-based networks require less cabling and equipment, making them a more affordable and scalable option for broadband expansion in underserved areas.
-
Supports up to 32 subscribers per strand: A single fiber strand in a TAP network can typically serve up to 32 endpoints, making it a practical solution for distributed service delivery.

How TAP Architecture Works
In a TAP-based network, a fiber cable runs through a service area, and fiber-optic taps are spliced into the line at various points. These taps divert a portion of the optical signal to individual subscribers while allowing the remaining signal to continue down the line. This process is repeated until the signal reaches its limit, typically serving up to 32 subscribers per fiber strand.
Comparison to Traditional Splitter-Based Networks
Unlike centralized splitter-based FTTH networks, which rely on distribution cabinets to manage fiber connections, TAP architecture simplifies deployment by eliminating the need for large equipment installations. This design reduces cabling requirements, minimizes splicing complexity, and lowers overall deployment costs.
Advantages of TAP Architecture
TAP architecture offers several benefits, including reduced infrastructure costs, faster installation times, and improved scalability for rural broadband expansion. It is particularly effective in areas with difficult terrain or low population density, where traditional network designs may be less feasible.