Aurora Networks® (ANS) and RUCKUS® Networks are now Vistance Networks
What is the main difference between CMTS and CCAP?
A Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) is a system located at the headend or hub site of a cable network. It is responsible for managing data traffic between subscriber cable modems and the internet. CMTS handles both upstream and downstream data transmission over Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial (HFC) networks and supports services such as high-speed internet, voice over IP, and video streaming. Traditionally, CMTS systems are part of centralized architectures where all data processing occurs at the headend.
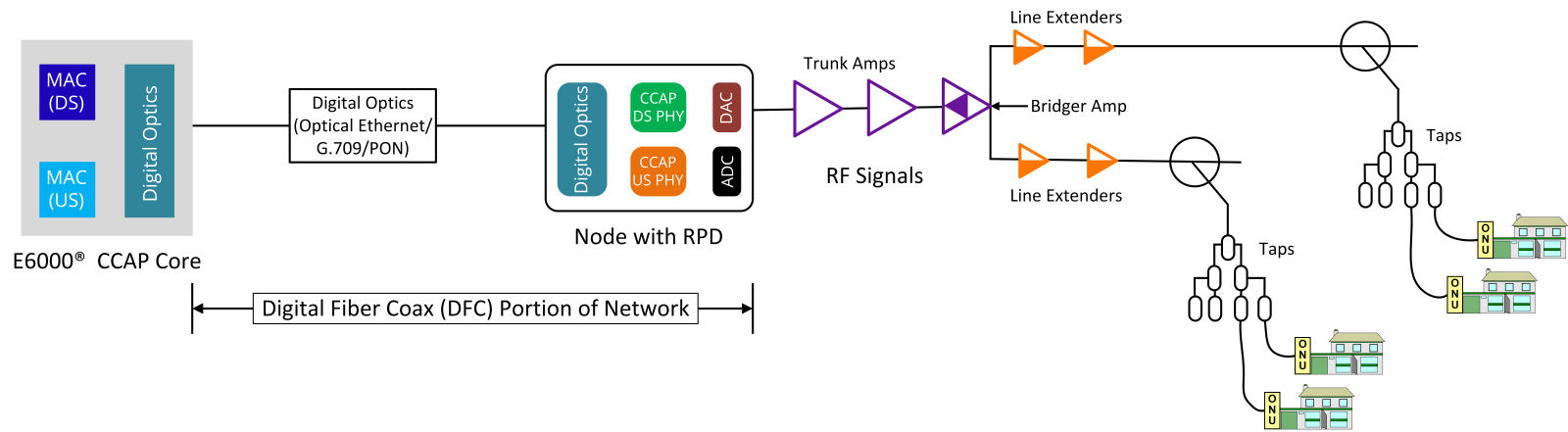
A Converged Cable Access Platform (CCAP) is a more advanced and integrated system that combines the functions of a CMTS and an Edge QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) device into a single platform. CCAP supports both data and video services over the same infrastructure, allowing operators to streamline their network architecture. It is designed to support higher service group density, improved power efficiency, and greater scalability. CCAP can be deployed in both centralized and Remote PHY and Remote MACPHY distributed access architectures.
Key Takeaways
- CMTS handles only data services, while CCAP integrates both data and video delivery into a single platform, reducing the need for separate equipment.
- CCAP supports higher service group density and is designed for more scalable and efficient broadband delivery compared to traditional CMTS systems.
- CCAP is compatible with distributed access architectures, enabling digital fiber links and remote processing, which improves network performance and flexibility.
- CMTS is typically used in centralized architectures, making it more suitable for legacy systems, whereas CCAP is better aligned with modern network evolution.
- CCAP offers operational advantages, such as reduced space and power requirements, simplified maintenance, and easier upgrades, making it a more future-ready solution.

Key Architectural Difference
The primary difference between CMTS and CCAP lies in their architectural scope and integration. CMTS focuses solely on data services and typically requires separate equipment for video delivery. In contrast, CCAP integrates both data and video capabilities, reducing the need for multiple devices and simplifying network management. This convergence allows for more efficient use of space, power, and cooling resources in the headend.
Support for Modern Network Evolution
CCAP is better suited for modern broadband networks that are transitioning to distributed access architectures. It supports digital fiber links and remote devices, enabling operators to move processing closer to the subscriber and improve network performance. While CMTS remains relevant in legacy systems, CCAP provides a more flexible and future-ready platform for delivering high-speed broadband and advanced services.
Operational Efficiency and Scalability
From an operational standpoint, CCAP offers enhanced scalability and resource optimization. Its modular design allows operators to expand capacity as needed without major infrastructure changes. This makes CCAP a more cost-effective and adaptable solution for growing broadband demands compared to traditional CMTS systems.
CommScope Related Links
Cable Modem Termination Systems (CMTS) & Converged Cable Access Platforms (CCAP)